
So, how does an organization choose a particular access control model? Let’s flash forward to the present, where Zero Trust has eclipsed traditional controls as it goes beyond the restrictions of a physical VPN and offers a more granular level of security that can benefit any business, regardless of size or industry sector. Another problem SMEs face is that many do not have dedicated IT staff and must outsource their security plan. If the appropriate defensive measures aren’t set in place, they could very well be out of business. According to a recent study by Accenture, over 43% of SMEs are the target of a cyber attack. On the flip side, smaller businesses will have a lot more to worry about as they are far less equipped to handle a major breach. An enterprise will require much more extensive and complex access controls to secure thousands of employees, entire departments, and third-parties from sophisticated cyber attacks.
DEFINE MANDATORY ACCESS CONTROL HOW TO
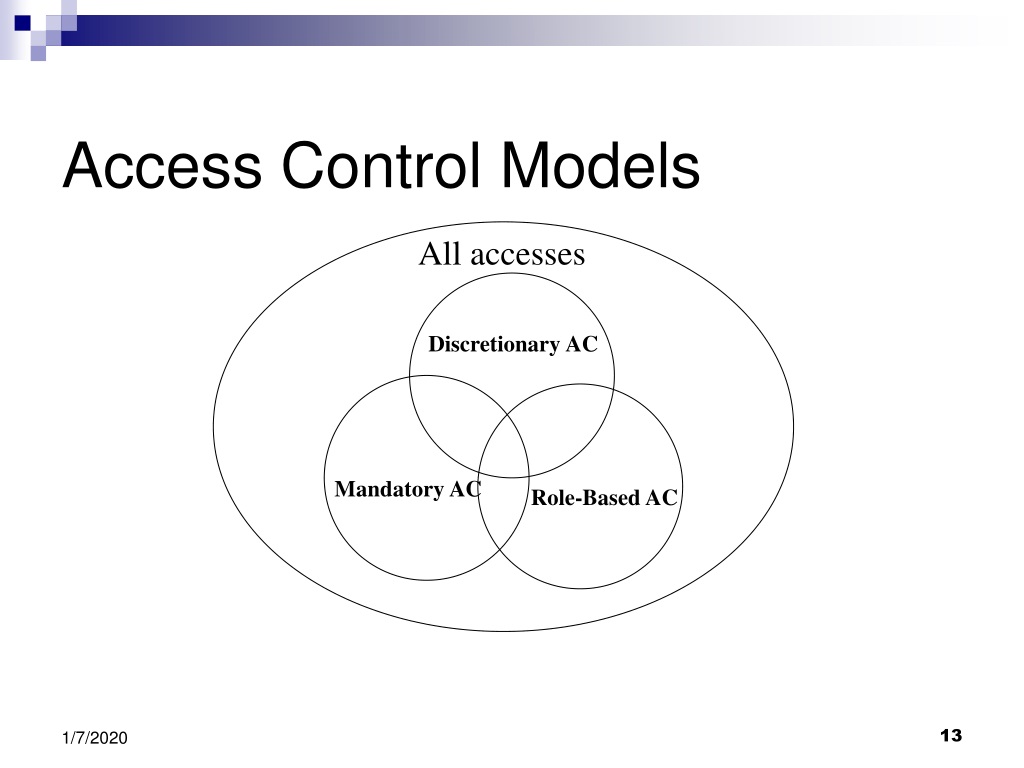
How to Choose the Right Access Control to Implement in Your OrganizationĮvery business is different. We will also list the advantages and disadvantages of each access control model in the current evolving hybrid workplace. We’ll take a closer look at four of the most common access control models PAM, MAC, DAC, and RBAC. In fact, 99% of all misconfigurations in the public cloud go unreported. Failure to restrict access can have great repercussions.

Going Beyond Traditional Access Controls with Perimeter 81’s Zero Trust ApproachĪccess controls are responsible for determining who can access certain resources in an organization.How to Choose the Right Access Control to Implement in Your Organization.
DEFINE MANDATORY ACCESS CONTROL MAC
It could be considered a confidentiality stamp. Label: a security attribute which can be applied to files, directories, or other items in the system. As the level increases, its security is considered to elevate as well. Level: the increased or decreased setting of a security attribute. As the integrity of the data is elevated, so does the ability to trust that data. Integrity: the level of trust which can be placed on data. Compartments make it possible to implement a need-to-know-basis security policy. A compartment represents a grouping, such as a work group, department, project, or topic. Periodicals, Journals, and MagazinesĬompartment: a set of programs and data to be partitioned or separated, where users are given explicit access to specific component of a system. Common Address Redundancy Protocol (CARP) File and Print Services for Microsoft® Windows® Clients (Samba) Mandatory access control (MAC) is an approach for restricting access to computer files and data based on the sensitivity (political, military, industrial, etc.). Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) Locale Configuration for Specific Languages FreeBSD as a Guest on VMware Fusion for macOS® FreeBSD as a Guest on Parallels Desktop for macOS® RAID3 - Byte-level Striping with Dedicated Parity GEOM: Modular Disk Transformation Framework Installing Applications: Packages and Ports Network Interfaces, Accounts, Time Zone, Services and Hardening


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
